
Service Information
Gin Poles
A steel gin pole is an essential lifting device required to install guyed and self supporting towers as well as antennas, lines and other tower equipment. Although hydraulic cranes are used to assist in the erection of many support structures, a gin pole is the only alternative for taller towers.
Most gin poles are constructed of triangular or square lattice shapes. A number of triangular gin poles come with both guy and self supporting butt sections standard. Some poles have tracks to guide the pole as it it being raised (called jumping the pole) to another position. Oftentimes the mast is tapered at the top and bottom of the pole to allow room for rigging equipment as well as having the ability to turn the tower section.
Some components of a gin pole system include:
- Load Line

This wire rope line is utilized to raise and lower the load. Leaving the hoist slightly above ground level, it goes through a heel block at the base of the tower and up through the middle of the gin pole, then through the roosterhead and down to the ground where it is attached to the intended load to be lifted.
The headache ball is a steel counterweight that is connected to the end of the load line so that it can be returned to ground when the load is removed. Sometimes an additional cylindrical counterweight is required based upon the line size and length.
- Jump Line

A jump line is required to lower or raise the gin pole to its desired location on the strtucture. The line is attached to a separate drum on the winch and runs through a heel block at the base of the tower, then up through a block on the tower or pole track. It proceeds through a series of blocks or to a set pole position.
- Roosterhead
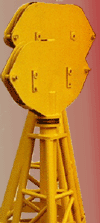
A roosterhead is attached to the top of the gin pole. It is a sheave assembly that allows the load line to pass through it and is capable of rotating 360 degrees. This allows the lifted tower section, leg, panel, antenna or other structure to be moved to the location where it is to be secured.
The tag line is used to control the load during the lifting or lowering process. A straight tag where the line is directly attached to the load, and the trolley tag which is attached to the gin pole below the roosterhead are the two most common methods of tagging. Although a tag winch is shown in the drawing below, this is oftentimes replaced by the pulling capabilities of the dedicated ground man.
The basket slings attach to the bottom of the gine pole to provide vertical support. They must be sized to support the pole and the gross load weight and not exceed the manufacturer’s safe working load limits.
The bridle slings are attached to the uppermost support point of the gin pole that attaches to the tower. They will restrict the pole from moving horizontally.
Capacity a function of three variables
Gin pole capacity is a function of three primary considerations:
1. Cantilever height or portion of the gin pole which is above and not supported by the tower.
2. Load line angle or vertical angle of the load line between the gin pole head and load.
3. Tag line angle or the angle between horizontal and the tag line.
New standard will increase gin pole safety
TIA-1019, the Structural Standards for Steel Gin Poles Used for Installation of Antenna Towers and Antenna Supporting Structures was approved and released in 2004 and provides an excellent tool to ensure that there is a greater awareness of safety during gin pole use. Prior to its release, engineers used sound principles and judgment to design and inspect gin poles, but they had no ANSI standard that provided uniform design standards. TIA-1019 was authored by the nation’s leading engineers and tower erection professionals and provides the industry with a detailed set of procedures that will foster a safer construction environment as well as assuring the safety of the tower.
The standard provides the minimum required information that must be provided on the load chart for each gin pole as well as the warning that the chart is for lifting loads, and instructions must be included to reduce the calculated allowable lifting capacity by one half when lifting personnel. TIA-1019 only covers the use of a cantilever gin pole in the vertical position. calculated allowable lifting capacity by one half when lifting personnel. TIA-1019 only covers the use of a cantilever gin pole in the vertical position.
Check bolts prior to reuse
Bolts should be checked each time they are to be used to connect your gin pole sections together. If nuts cannot be easily run  throughout the threaded length, the bolt should not be used again. A bolt less than ¾” in diameter should not be used twice unless an engineer provides specifications for an appropriate procedure of testing prior to reuse. Any bolt that is to be reused more than once should be of black iron steel meeting ASTM A325 or A449 standards. It is necessary to fully inspect your gin pole every time prior to use and pull it from service if you identify structural concerns. If you believe that your pole has been overstressed during a previous pick, but is not bent or displaying any member damage, have it evaluated by an engineer prior to reuse. throughout the threaded length, the bolt should not be used again. A bolt less than ¾” in diameter should not be used twice unless an engineer provides specifications for an appropriate procedure of testing prior to reuse. Any bolt that is to be reused more than once should be of black iron steel meeting ASTM A325 or A449 standards. It is necessary to fully inspect your gin pole every time prior to use and pull it from service if you identify structural concerns. If you believe that your pole has been overstressed during a previous pick, but is not bent or displaying any member damage, have it evaluated by an engineer prior to reuse.
Obtain engineering for existing poles
It is advisable to get your existing gin poles reviewed by a qualified engineer to ensure that they meet the TIA-1019 standard. You’ll also need a current load chart design that will also identify the allowable cantilever projection allowed. All new poles must be designed to TIA-1019. Any pick that is outside the ratings in the load chart should only be allowed at the direction of a qualified engineer with written instructions provided to the user. Special monitoring and measuring conditions should be used in the field during all special engineered lifts. engineer to ensure that they meet the TIA-1019 standard. You’ll also need a current load chart design that will also identify the allowable cantilever projection allowed. All new poles must be designed to TIA-1019. Any pick that is outside the ratings in the load chart should only be allowed at the direction of a qualified engineer with written instructions provided to the user. Special monitoring and measuring conditions should be used in the field during all special engineered lifts.
Gross load weights categorize gin poles
Based upon a cantilever height of 40% of the overall length of the gin pole and other requirements, the national standard classifications include:
- Class A 0 < 1,000-pounds gross load
- Class B 1,000 < 3,000-pounds gross load
- Class C 3,000 < 10,000-pounds gross load
- Class D 10,000-pounds and over gross load
We recommend that you purchase a copy of TIA-1019 to ensure that your gin pole is structurally sound and provides a safe working environment for your employees.
 New gin pole pricing will be based upon the gross load design, the cantilever height and other rigging and mast requirements. Budgetary estimates for the following poles are: New gin pole pricing will be based upon the gross load design, the cantilever height and other rigging and mast requirements. Budgetary estimates for the following poles are:
Is it Jim, Gyn, Jin or Gin? 
Although there are numerous spellings for this piece of erection equipment, the most common and correct term is "gin" as in enGINe which refers to any mechanical device that transfers energy into movement. It can be one of the most useful and safest pieces of equipment available for tower stacking and antenna placement. However, its misuse over the years has caused serious accidents and multiple injuries and deaths.
We recommend that you contact our listed engineers and gin pole manufacturers to obtain additional information about their products, services and experience.
|