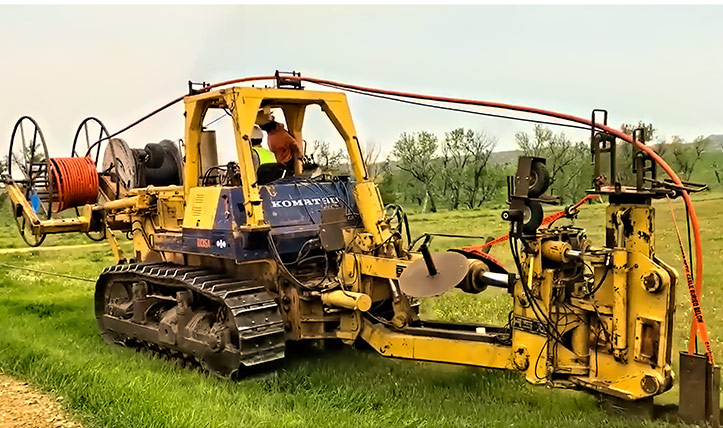
The Fiber Broadband Association has announced the results of its 2023 Fiber Deployment Cost Study, conducted by Cartesian, which provides the industry’s benchmark to help fiber broadband service providers evaluate their cost profile and identify areas of inefficiency. FBA’s comprehensive study identifies that, on average, labor contributed to 73% of underground build costs and 67% of aerial costs. The study also provides regional cost variations, along with the cost differential between deployment methods.
“As broadband providers across the country look to leverage public and private funding to connect communities to high-quality broadband services, understanding the cost variables of deployment remains a vital component to broadband plans and proposals,” said Deborah Kish, Vice President of Research and Workforce Development at the Fiber Broadband Association. “Our annual Fiber Deployment Survey uncovers fiber cost benchmarks and how costs change over time—information that is critical for broadband providers and state broadband offices as they prepare competitive applications for NTIA BEAD funding to connect their communities to reliable fiber broadband services.”
The 2023 Fiber Deployment Study survey respondents spanned across the U.S. and the fiber deployment ecosystem including network operators, municipal broadband providers, utility/electric cooperatives, prime contractors, and subcontractors. The study explored many factors that influence cost but often make it challenging to compare costs across deployments. This includes cost components like labor, materials, build scenarios, and the choice of construction method.
While no two deployment projects were alike, the study found several common themes. These themes include that labor accounts for over two-thirds of build costs; the initial cost per foot for aerial deployment is less than half that of underground, but higher OpEx of aerial negates the cost differential in the long run; and other notable cost influencers like population density, terrain, and region.
Looking forward to 2024, many respondents expected overall deployment costs to continue to increase, but several categories were expected to improve. In 2023, 76% of respondents noted cost increases in materials, but only 58% of respondents expected materials cost to increase in 2024.